Depression, eine psychische Störung mit hoher Prävalenz, leichte Rückfälle und hohe Selbstmordrate. Unter den verschiedenen Behandlungen, Medikamente neigen dazu, Patienten abhängig zu machen, Während die Langsamkeit und die künstliche Unsicherheit der Psychotherapie eine Reihe von Schwierigkeiten bei der Behandlung dieser Krankheit mit sich bringen.
In den letzten Jahren, Forscher haben auf alternative Wege zur kontaktlosen Phototherapie hingewiesen, and more and more studies have pointed out that red light phototherapy provides energy for the body and produces biological effects, which can play an antidepressant role, and can be used as an adjunctive treatment for depression and other mood disorders.

Red light enhances neuroprotection and metabolic function
The etiology of depression is complex, the pathogenesis is unknown, and the disease varies from person to person, but mitochondrial dysfunction in various regions of the brain has been revealed to be closely related to the pathology of depression in journals such as Current Neuropharmacology, Nature, usw. Mitochondrial damage affects the process of ATP production, which impairs neuroplasticity, and thus participates in the process of depressive disorders.
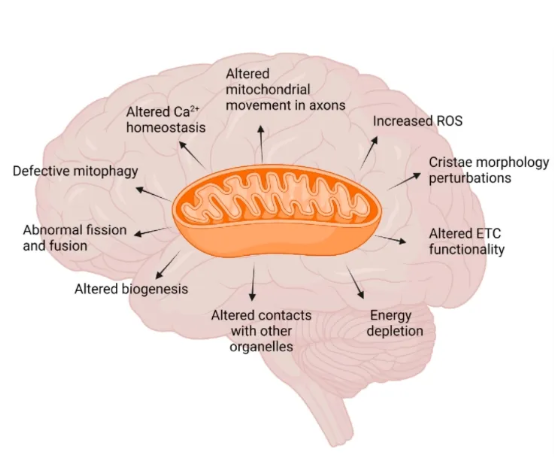
A research team from City University of Hong Kong found that mitochondria are the largest absorbers of red light. Red light irradiation can increase mitochondrial catalase activity, which can activate sugar metabolism and important enzymes of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, increase the level of endogenous insulin, and promote the utilization of sugar and the production of ATP, thus promoting cell synthesis, was der Reparatur und Regeneration von beschädigten Geweben förderlich ist, and then stimulate the nerve tissue to achieve therapeutic purposes.

Red light has multiple regulatory mechanisms to improve depressive behavior
Red light upregulates anti-inflammatory factors to avoid neuroinflammatory responses
Zusätzlich, there are several hypotheses for the pathogenesis of depression, among which the inflammatory response is closely related to the intractability of depression. And a growing body of data suggests that peripheral inflammatory factors, such as interleukin 6, can cross the blood-brain barrier and thus induce depression.
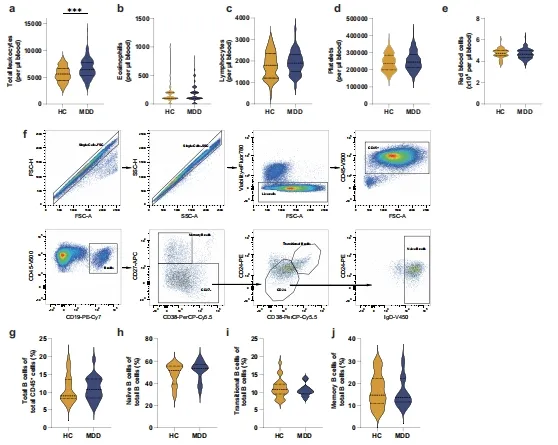
Comparison of leukocyte subpopulation frequencies in patients with major depression
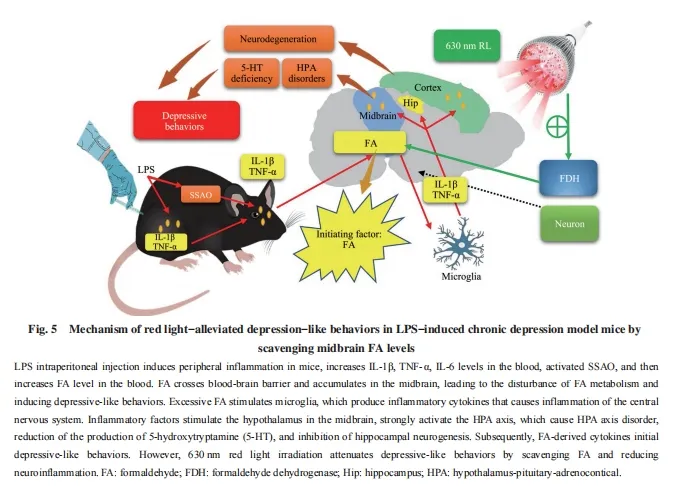
A team from Wenzhou Medical University and Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Neurology Research found that red light irradiation can directly activate FDH (formate dehydrogenase) and cytochrome c (hemoglobin that regulates apoptosis), which not only avoids neurocytotoxicity caused by sustained elevation of glycolysis in early stages of depression, but also avoids involvement in triggering a neuroinflammatory response. affecting neuronal cell metabolism, thereby improving depressive-like behavior in mice.
Red light modulates neurotransmitters and promotes happy dopamine production
Reduced functional activity of monoaminergic neurotransmitters is also recognized as one of the important hypothesized mechanisms in the development of depression. Whereas tetrahydrobiopterin is an essential cofactor in the synthesis of its transmitters (Dopamin und 5-Hydroxytryptamin), its reduced levels can increase the susceptibility to depressive episodes.
A clinical study by renowned biologists Hoekstra, Lambert and others found that 19 patients treated with red light had increased levels of tetrahydrobiopterin and enhanced dopaminergic transmission in most brain regions, with effects on rhythmic behavior.

Red light promotes regularity of work and rest and restores the biological clock to homeostasis
It is worth mentioning that many studies have also indicated that the pathogenesis of depression is closely related to the disruption of biological rhythms, vor allem saisonale Depression. It has been shown that red light inhibits the secretion of melatonin, which regulates circadian rhythms and promotes sleep, and this is believed to be one of the mechanisms of its antidepressant action.
Famous biologists Virk and Krivisky used red light irradiation in untreated seasonal affective disorder patients, which can inhibit the pineal gland by activating photosensitive retinal ganglion cells, reduce the synthesis and release of melatonin during the daytime, and restore homeostasis of the biological clock to indirectly regulate the moods of patients with depression and found that a brief irradiation of less than 20 min has a significant clinical effect.
Red light clinically proven to play a positive role in depression
Numerous studies on the mechanism of red light irradiation and a large number of clinical trials have confirmed that red light is effective in exerting an antidepressant effect when it is involved in the reduction of inflammation, oxidative stress levels, promotion of metabolism, regulation of apoptosis, and other processes.
MERICAN Health Pod is based on red light therapy, and combines a variety of specific wavelengths of light on the whole body skin to produce biological effects, to promote the enzyme, mitochondria as a medium, prompting hundreds of genes to express the impact of the blood circulation to the immune regulation and the various cellular processes of repair and protection, and then activate the activity of nerve cells, the secretion of neurotransmitters so that the neural pathway to produce physiological changes in the organism’s It regulates the circadian rhythm, mood and sleep, and effectively relieves depression.
Basierend darauf, the MERICAN Light Energy Research Center and the German team, together with a number of universities, scientific research and medical institutions, randomly selected a number of males and females aged 20-55 years old with depressive moods and behaviors as the research subjects, and then supplemented them with the MERICAN Health Chamber for light therapy testing under the guidance of a healthy lifestyle, and the types and dosages of the medications taken during the entire testing process remained unchanged.

Nach 3 months of regular 30-minute exposure to the health pod, it was found that the subjects’ Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD) and Self-Depression Scale (SDS) scores were significantly lower than before treatment, and the Psychological Adaptability Scale was also substantially higher than before treatment, with a significant reduction in depressive symptoms, and a reduction in daytime somnolence, and an earlier and better night’s sleep that night. Gleichzeitig, the recovery of physical fitness was remarkable, and there was a significant improvement in memory and cognition.

It can be seen that red light phototherapy can play a positive role in regulating symptoms such as depression biorhythms and sleep disorders, and the daily use of MERICNA health pods can effectively alleviate and prevent depression, anxiety and other emotional problems.


























