Verständnis der Struktur und Funktion des Gehirn
Das menschliche Gehirn ist hochorganisiert, vielschichtiges Organ, das nahezu jeden Aspekt der körperlichen und geistigen Funktion steuert. Es ist normalerweise in drei Hauptregionen unterteilt:
- Großhirn: Der größte Teil des Gehirns, verantwortlich für bewusstes Denken, Erinnerung, freiwillige Bewegung, und Sprache.
- Kleinhirn: Unterhalb des Großhirns positioniert, es koordiniert die Körperhaltung, Gleichgewicht, und präzise motorische Aktivitäten.
- Hirnstamm: Verbindung des Gehirns mit dem Rückenmark, Es reguliert wesentliche autonome Funktionen wie den Herzschlag, Atmung, und Schlaf-Wach-Zyklen.
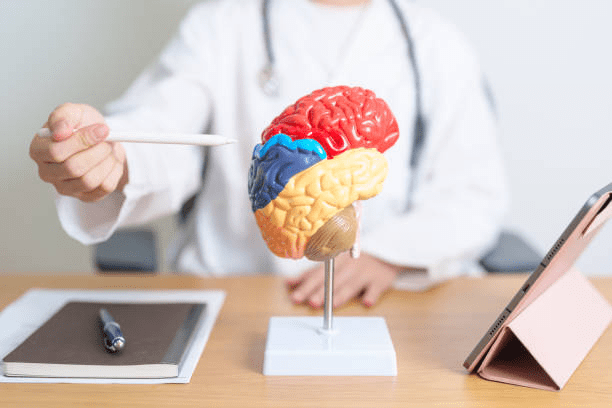
Über diese strukturellen Unterteilungen hinaus, Das Gehirn besteht aus hochspezialisierten Regionen mit unterschiedlichen Verantwortlichkeiten:
- Hirnrinde: Die äußere Schicht des Großhirns, verantwortlich für höhere kognitive Prozesse wie das logische Denken, Aufmerksamkeit, Sinneswahrnehmung, und Entscheidungsfindung. It’s further divided into four lobes—frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital—each managing different functions.
- Subcortical Structures: Including the hippocampus (memory processing), amygdala (emotion regulation), and basal ganglia (movement control).
- Neurotransmitter Networks: Systems like the dopaminergic and serotonergic pathways influence mood, behavior, and reward mechanisms.
- Glial Cells: Often overlooked, these support and protect neurons, playing a key role in immune defense and homeostasis within the brain.
From infancy to adulthood, billions of synaptic connections are created or eliminated in response to learning and experience. This process—called synaptic pruning and neural plasticity—continues through life, allowing the brain to adapt and reorganize.
It is this very adaptability that makes the brain responsive to external stimuli like red light. Increasing research is now investigating how red light therapy may influence these neural circuits, potentially “rewiring” the brain in ways that improve cognition, Stimmung, and overall neurological function.
What Happens in the Gehirn During Red Light Therapy?
How Red Light Reaches and Influences the Human Gehirn
Rotlichttherapie (RLT) uses specific wavelengths—typically in the range of 630–850 nanometers—to deliver low-level light energy through the scalp.
Red and NIR wavelengths penetrate the scalp and skull with relative ease compared to other light types. Once they enter the brain, they stimulate photoreceptors in the mitochondria—especially the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme.
This stimulation leads to several downstream effects:
- Erhöhte ATP-Produktion: Providing neurons with more energy to carry out repair and signaling.
- Reduced oxidative stress: Lowering inflammation levels within brain tissue.
- Improved cerebral blood flow: Enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery to targeted regions.
Red light interacts with neuronal tissues and triggers cellular processes that may improve neuroplasticity and reduce inflammation—both of which are essential for supporting cognitive health and potential brain mapping and red light therapy applications.
The Biological Mechanisms Behind Red Light Therapy
Mitochondrial Activation
Red light photons stimulate cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria, the enzyme responsible for cellular respiration. This enhances ATP (Adenosintriphosphat) Produktion, supplying neurons with the energy required for repair, synaptic transmission, and regeneration.
Vasodilation and Blood Flow
Nitric oxide release from mitochondrial stimulation leads to vasodilation. This increases regional cerebral blood flow, enabling better oxygen and nutrient delivery to neural tissue—vital for maintaining long-term brain function.
Anti-inflammatory Signaling
Red light reduces oxidative stress by modulating reactive oxygen species (Ros) Ebenen. This contributes to the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the brain, which is particularly relevant for neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity
RLT has been shown to increase the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports neuron growth, survival, and synaptic remodeling. This process is central to red light therapy’s proposed role in promoting red light for nerve repair.
Red Light’s Impact on Common Brain Disorders
Red light therapy is being investigated as a supportive treatment for several major brain disorders, particularly those with chronic inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction at their core.
A pilot study found that red/NIR light therapy significantly improved executive function and memory in chronic mTBI patients, suggesting potential neuromodulation effects on the prefrontal cortex.
Red Light Therapy for Neurological Disorders and Cognitive Decline
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Red light may reduce beta-amyloid accumulation and oxidative stress, while improving memory performance in early-stage patients.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Animal models show red light can protect dopaminergic neurons and improve motor coordination.
- Depression and Dementia: Chronic depression is linked to hippocampal atrophy, increasing dementia risk. Red light’s anti-inflammatory and neurogenic effects could help restore hippocampal integrity and cognitive balance.
- Angst: Red light therapy anxiety protocols have shown promising outcomes in reducing stress-related behaviors and regulating emotional processing centers in the brain.
Red Light Therapy vS. Conventional Therapies
| Behandlung | Estimated Cost | Brain Region Targeted | Wirksamkeit | Risk/Side Effects |
| Rotlichttherapie | $500–$1,000 (device) | Prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala | Enhances energy metabolism, neuroplasticity, mood balance | Minimal; low risk when used properly |
| Alzheimer’s Medication | $3,000+/year | Hippocampus, temporal cortex | Slows memory decline, does not halt progression | Gastrointestinal issues, Schwindel, long-term toxicity |
| Parkinson’s DBS | $35,000–$50,000 (one-time) | Basal ganglia, thalamus | Strong motor improvement, invasive but effective | Infection, hemorrhage, device complications |
| SSRIs (Depression) | $1,000+/year | Prefrontal cortex, limbic system | Reduces symptoms; variable response | Sexual dysfunction, Gewichtszunahme, emotional blunting |
| Psychotherapy | $100/session (~$3,000/year) | Prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala | Long-term cognitive and emotional benefits | Low physical risk; dependent on therapist and duration |
As research into brain mapping and red light therapy continues to evolve, this approach may serve as both a primary and adjunctive treatment, especially for patients seeking safer and more sustainable options.
Practical Recommendations for Maintaining Brain Health
Für optimale Ergebnisse, red light therapy should be combined with other brain-supportive habits:
- Nutrient-dense diet: Include omega-3s, Antioxidantien, and B-complex vitamins
- Regelmäßige Bewegung: Aerobic activity enhances cerebral blood flow
- Sleep hygiene: Konsistent, deep sleep supports neural repair
- Mental engagement: Reading, learning, and social interaction preserve cognitive flexibility
- Routine therapy: Use red light devices 3–5 times per week for cumulative effects
How to Use Red Light Therapy to Support Brain Health at Home
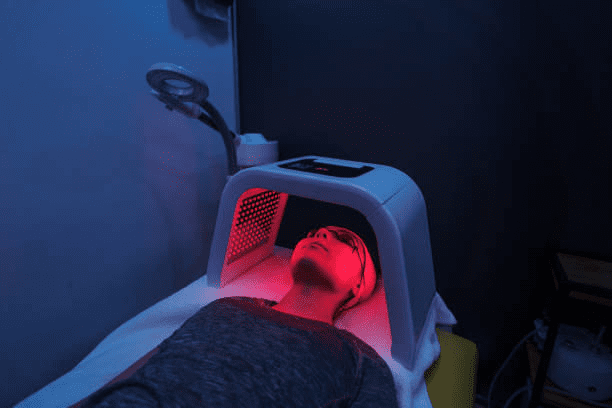
Best Wavelengths and Recommended Devices for Brain Stimulation
- Ideal Wavelengths: 810–850nm is most effective for penetrating the skull and reaching the brain.
- Bestrahlungsstärke: 20–100 mW/cm² is appropriate for neuro applications.
- Sitzungsdauer: 10–20 Minuten pro Bereich, 3–5 Mal pro Woche.
- Recommended Devices:
- LED Leder Beauty Mask MM04 (630–850 nm, CE-certified, targeted facial and cognitive therapy)
- Rotlichttherapie Panel MP03 (660/850nm, FDA-listed, full-head and prefrontal coverage)
- Rotlichttherapiebett M4 (660/850nm, medizinische Qualität, whole-body support including neurological targets)
Safety and Usage Guidelines for Red Light Therapy on the Brain
- Use protective goggles when applying light near the eyes.
- Begin with short sessions and gradually increase exposure.
- Avoid use if you have photosensitivity, Epilepsie, oder sind schwanger.
- Befolgen Sie die Anweisungen des Herstellers und wenden Sie sich bei chronischen Erkrankungen an einen Fachmann.
- Die Rotlichttherapie ist im Allgemeinen sicher, Bei bestimmungsgemäßer Verwendung sind keine Nebenwirkungen bekannt.
Rotlichttherapie und Brain-Tech-Innovation
Die Rotlichttherapie verändert nicht nur unsere Denkweise über Heilung – sie wird auch Teil eines umfassenderen technologischen Ökosystems, das auf die Optimierung der Gehirnleistung abzielt.
- Gehirnkartierung und Rotlichttherapie: Moderne bildgebende Verfahren (wie fNIRS und EEG) werden jetzt neben Rotlicht verwendet, um Veränderungen der Aktivität und des Blutflusses in Echtzeit sichtbar zu machen.
- Gehirn-Computer-Schnittstellen (BCIs): In der Frühphase der Forschung wird untersucht, wie die Stimulation mit rotem Licht kognitive Kontrollsignale in BCI-Anwendungen verbessern könnte.
- KI-personalisierte Therapie: Einige Startups verwenden KI-Algorithmen, um biometrische Daten zu analysieren und Rotlichtbehandlungsprotokolle für einzelne Benutzer zu optimieren.
Diese Integrationen könnten bald eine neue Ära der Nicht-Invasivität einläuten, adaptive Neurotherapien – sie geben Benutzern mehr Kontrolle über ihre Gehirngesundheit als je zuvor.
FAQs
Was bewirkt die Rotlichttherapie für das Gehirn??
Es steigert die mitochondriale Aktivität, Reduziert Entzündungen, und unterstützt die Neuroplastizität in Gehirnzellen.
Ist Infrarotlicht für das Gehirn ungefährlich??
Ja, Nahinfrarotlicht ist im Allgemeinen sicher, wenn es ordnungsgemäß mit kontrollierten Wellenlängen und Intensitäten verwendet wird.
Was ist der Unterschied zwischen Infrarot- und Rotlichttherapie-Gehirn??
Rotes Licht zielt auf oberflächliches Gehirngewebe; Nahinfrarot dringt tiefer ein und sorgt für stärkere neurologische Effekte.
Kann eine Rotlichttherapie die Gehirnfunktion verbessern??
Studien deuten darauf hin, dass es das Gedächtnis verbessern kann, Stimmungsregulierung, und Blutfluss in bestimmten Gehirnregionen.


























