Diabetes mellitus, uma doença crônica em que anormalidades hormonais endócrinas causam concentrações excessivas de glicose no sangue, desencadeando danos a múltiplos órgãos.
O número de adultos com idade 20-79 anos com diabetes em todo o mundo 2021 é um tremendo 537 milhão, ou 7 fora de 100 pessoas com diabetes. Evitando comida, medir a glicemia e tomar insulina todos os dias traz inúmeros problemas de vida e ansiedade psicológica para a maioria dos pacientes e suas famílias.
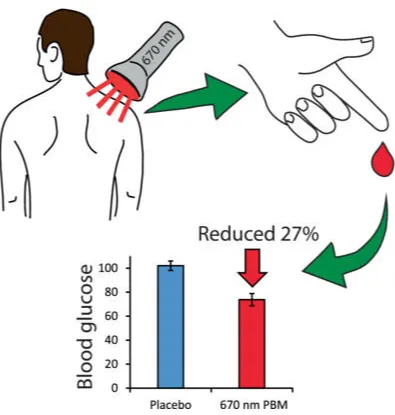
Felizmente, “Science and Technology Daily” recentemente uma notícia pesada, para a maioria dos “amigos do açúcar” para trazer boas: Faculdade da Cidade de Londres, os cientistas da Universidade de Londres e da University College London trabalharem juntos para realizar as pesquisas mais recentes mostram que 670 irradiação de luz vermelha nanométrica nas costas de uma pessoa para 15 minutos, pode reduzir os níveis de açúcar no sangue!
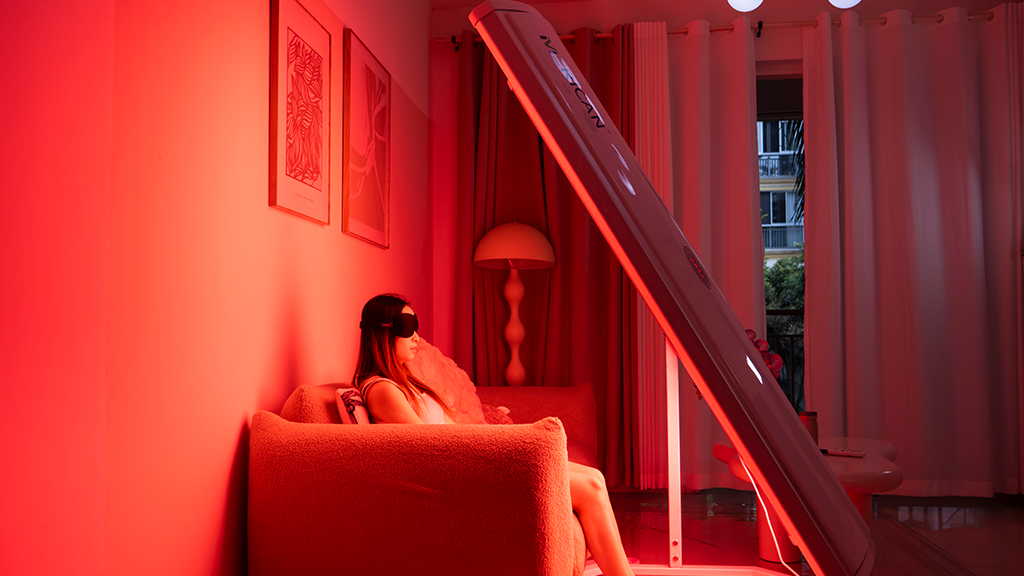
A irradiação da luz vermelha reduz a devastação do açúcar no sangue
O diabetes em si não é assustador, são as complicações que são assustadoras, e o DCCT (Teste de controle e complicações do diabetes) e estudos europeus há muito que confirmam que o controlo do açúcar no sangue pode retardar eficazmente o desenvolvimento de complicações tanto nos tipos 1 e digite 2 diabetes.
A abordagem usual para controlar a glicemia é a intervenção no estilo de vida com administração oral de algum tipo de medicamento hipoglicemiante.. No entanto, à medida que a doença progride, será cada vez mais difícil reduzir a glicemia, e vários agentes hipoglicemiantes, até insulina, será gradualmente necessário para controlar a glicemia. Esses tratamentos medicamentosos invasivos podem trazer efeitos colaterais inesperados aos pacientes. E como um método não invasivo, técnica não farmacológica conhecida por sua segurança, fisioterapia da luz vermelha tem potencial para minimizar efeitos colaterais e trazer mais benefícios aos diabéticos.
Acontece que, as mitocôndrias são conhecidas como “fábricas de energia” celulares, que utilizam oxigênio e glicose para produzir trifosfato de adenosina (ATP), que fornece energia para processos celulares importantes no corpo. Quando 670 nm luz vermelha estimula mitocôndrias, o potencial de membrana mitocondrial e produção de trifosfato de adenosina (ATP) pode ser aumentado através da fotobiomodulação (PBM), um processo que aumenta a demanda e o consumo de glicose, reduzindo assim os níveis de glicose no sangue.
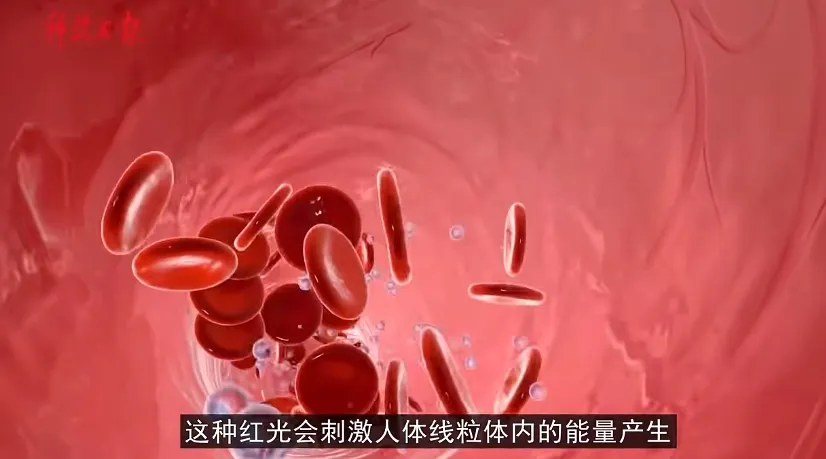
Experimentos mostraram que esta estimulação da luz vermelha reduziu os níveis de glicose no sangue em 27.7% após a ingestão de glicose e reduziu os picos máximos de glicose em 7.5%. De acordo com o Dr.. Bonner, the lead author of the study, says we can use a single 15-minute exposure to red light after eating to help reduce potentially damaging glucose spikes in the body after a meal.
This latest study, published in the German Journal of Biophotonics, a leading international scientific journal, suggests that Although this study was conducted in healthy individuals, its non-invasive, non-pharmacological technique has the potential to positively impact postprandial diabetes control by reducing the damaging fluctuations in blood sugar in the body that lead to aging.
Dr. Bonner, Senior Lecturer in Neurobiology at the School of Health and Psychological Sciences at City, and Professor Geoffrey, Professor of Neuroscience at the Institute of Ophthalmology, University College London, also said that this improvement in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from nucleosides leads to changes in signaling that propagate throughout the body.
Red light is widely used in recreational therapy
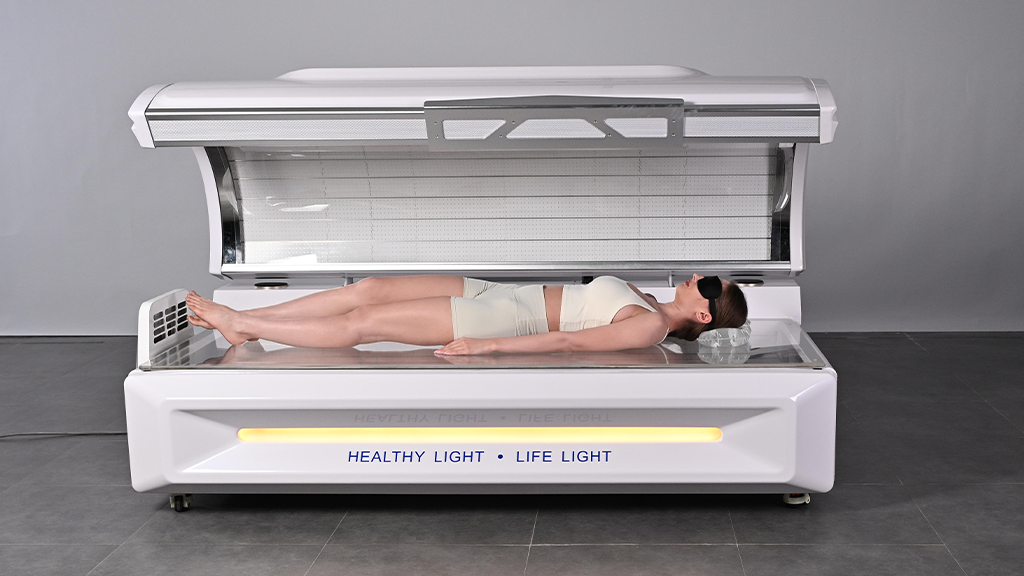
Fotobiomodulação (PBM) of red light is primarily photochemical, not thermal. The effect achieved by red light irradiation is mainly through the transfer of red light energy into cells to stimulate new cellular vitality.
Earlier authoritative studies have confirmed that long-wavelength light between about 650-900 nm (from the visible to near-infrared range) increases mitochondrial ATP production, which lowers blood glucose and improves animal health and longevity. In previous studies, 670 nm light selectively irradiated to the backs of mice has been shown to improve ATP, and thus symptoms, in both a Parkinson’s disease model and a diabetic retinopathy model.

The maximum absorption of red light is mitochondria, red light irradiation increases the activity of catalase in mitochondria, which can increase the cellular metabolism, increase the content of glycogen (not only stores energy, but also breaks down into glucose to regulate the concentration of blood glucose), increase the synthesis of proteins and increase the decomposition of adenosine triphosphate to promote cell synthesis, healing of wounds and ulcers, hair growth and bone fracture healing, accelerate the regeneration of damaged nerves, increase White blood cell phagocytosis, remove free radicals in the body, so that the blood viscosity decreases and oxygen-carrying capacity significantly higher, regulate immune function, improve fat accumulation, delay skin aging, so red light in the clinic can treat a variety of diseases.
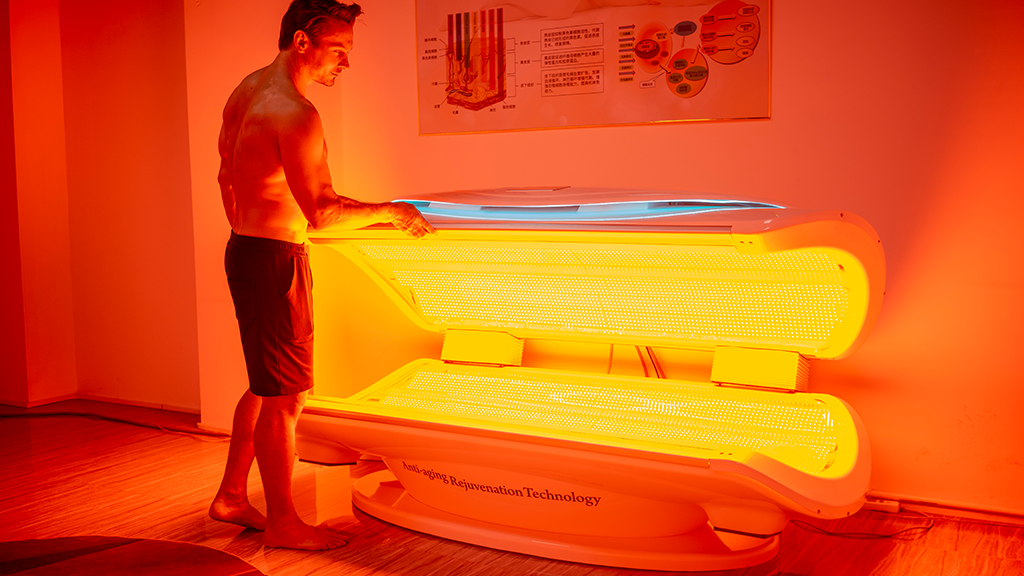

As a non-invasive, non-drug technology, red light physiotherapy is harmless and is used by many large tertiary hospitals to relieve patients’ dor.
Merican Light Energy Research Center and a number of universities, medical research institutions through a number of clinical verification has also proved that through a kind of red light irradiation called photodynamic health cabin, can penetrate 1-4cm under the skin, on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular and other circulatory system disease improvement, tissue and nerve pain repair, postpartum rehabilitation, as well as physical restoration and cosmetic surgery and so on, there are obvious effects. Together with the use of LED cold light source, light-emitting diode way for the light source, low heat generation, no thermal radiation, even if beyond the treatment time, will not produce thermal damage to the human body, and does not contain any radioactive substances.



























