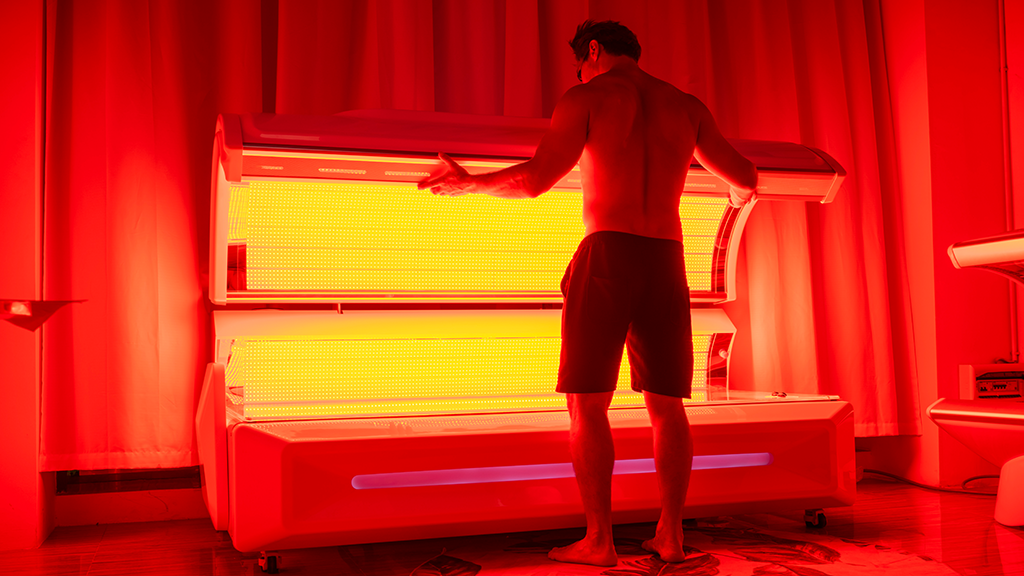
فعالية الضوء الأحمر: تبييض وتجديد الجلد, تناقص البقع, تنعيم التجاعيد, تشديد الجلد, تحسين بلادة, تأخير الشيخوخة,إلخ.
المؤشرات:العناية بالبشرة, ارتفاع نسبة الدهون في الدم,ارتفاع ضغط الدم وارتفاع نسبة السكر في الدم,حَبُّ الشّبَاب,آلام مختلفة,الالتهابات المختلفة,القلق والاكتئاب,الأكزيما,إلخ.
كيف يمكن للضوء الأحمر أن يؤثر على نومك
تستجيب إيقاعات الساعة البيولوجية – الساعة الداخلية للجسم التي تتحكم في دورات النوم والاستيقاظ – للضوء كإشارة للاستيقاظ, والظلام كإشارة للنوم,بحسب المراكز الأمريكية لمكافحة الأمراض والوقاية منها.
نحن أكثر حساسية للضوء ذو الطول الموجي الأزرق، وهو النوع المنبعث من الهاتف, شاشات التلفاز والكمبيوتر المحمول, وكذلك الشمس، وهو الضوء الذي وُجد أنه يمنع إفراز هرمون النوم الميلاتونين..
"خلال النهار, وذلك عندما تريد بالتأكيد الضوء الأزرق لأنك تريد قمع الميلاتونين أثناء النهار عندما يجب أن تكون مستيقظًا,قال داسغوبتا. "لهذا السبب نقول دائمًا, "اخرج وتعرض لأشعة الشمس الجيدة عندما تستيقظ في الصباح."
بحث عن الضوء الأحمر والنوم
لأن الضوء الأزرق يمنع إطلاق الميلاتونين, الفرضية التي تقوم عليها الأبحاث حول النوم والضوء الأحمر – اللون على الطرف الآخر من الطيف – هي أن الضوء الأحمر قد يشجع على إطلاق الميلاتونين., قال داسغوبتا.
ولكن لا يوجد سوى عدد قليل من الدراسات التي أجريت على مشاركين من البشر الأصحاء حول الضوء الأحمر والنوم, معظمها صغير الحجم, تتراوح من 10 ل 30 المشاركين لكل منهما. ويبدو أن دراستين فقط من هذه الدراسات قد وجدت مثل هذا الارتباط.
في 2012 يذاكر, قام باحثون مقيمون في الصين بتقييم تأثير العلاج بالضوء الأحمر على جودة النوم وتحمل الأداء 20 لاعبات كرة السلة الإناث. تلقى نصف اللاعبين 30 دقائق من تشعيع الجسم بالكامل من جهاز العلاج بالضوء الأحمر الذي يشبه سرير تسمير البشرة. ووجد الباحثون أن هذه المجموعة شهدت تحسنًا أكبر في النوم ومستويات الميلاتونين في الدم مقارنة بمجموعة الدواء الوهمي, التي لم تتلقى العلاج بالضوء الأحمر.
نظرا لمحدودية الأبحاث, "هذه واحدة من تلك المواقف التي يوجد فيها اختراق للنوم.",ولكن لا يوجد دليل وراء ذلك حقًا,قال جوشوا تال, طبيب نفساني مقيم في مدينة نيويورك متخصص في مشاكل النوم. "لا أرى فائدة."
وقد وجدت دراسات أخرى تأثيرًا مختلفًا تمامًا. "لقد أظهرنا أنه يمكنك بالفعل تنبيه الدماغ عن طريق تعريض الناس لهذا الضوء الأحمر المشبع,قالت ماريانا فيجويرو, مدير مركز ماونت سيناي لأبحاث الضوء والصحة في مدينة نيويورك.
أ 2019 بحثت دراسة أجراها فيجويرو في ما إذا كان توصيل الضوء الأحمر إلى العيون المغلقة أثناء النوم - باستخدام قناع الضوء الأحمر - وفتح العينين عند الاستيقاظ - عبر نظارات الضوء الأحمر - يقلل من القصور الذاتي أثناء النوم بين الأشخاص. 30 البالغين. القصور الذاتي أثناء النوم هو عملية يومية تعدل الذاكرة, مزاج, وقت رد الفعل واليقظة عند الاستيقاظ, وفقا ل 2015 يذاكر. يعاني بعض الأشخاص من ضعف الأداء والترنح خلال هذه الفترة الزمنية, وعادة ما تهدأ آثار القصور الذاتي أثناء النوم بعد ذلك 15 ل 60 دقائق ولكن يمكن أن تستمر لمدة تصل إلى بضع ساعات.
في دراسة فيجويرو, جمع المؤلفون بيانات عن نعاس المشاركين - الذي أبلغوا عنه ذاتيًا - بالإضافة إلى الأداء السمعي ومستويات الكورتيزول في ثلاث ليالٍ من أيام الجمعة على مدار ثلاثة أسابيع متتالية.. ووجدوا أن الضوء الأحمر يتم تسليمه من خلال عيون مغلقة بينما كان المشاركون نائمين، مما خفف من جمود النوم عند الاستيقاظ.
كما وجدت دراستان صغيرتان أخريان أجراهما فيجويرو أن الضوء الأحمر يحفز اليقظة.
"لن أدعي ذلك (الضوء الأحمر) يعزز النوم,قال فيجويرو, وهو أيضًا أستاذ في قسم علوم وسياسات الصحة السكانية في كلية إيكان للطب في جبل سيناء.
تأثير الضوء الأحمر على النوم
أولئك الذين يروجون للضوء الأحمر باعتباره مفيدًا للنوم من المحتمل أن يخلطوا بين الميل المنخفض للضوء الأحمر لقمع الميلاتونين وتحسين النوم - وهو ليس نفس الشيء, قال فيجويرو.
"الشيء الوحيد الذي يمكنك أن تجادل فيه هو أن ما تفعله هو, إذا أعطيت هذا الضوء الأحمر في المساء قبل النوم, أنت تقلل من تعطيل النظام اليومي, لأن اضطراب النظام اليومي يحدث مع الضوء الساطع أو الأزرق,قال فيجويرو. بعبارة أخرى, قد تكون أي فوائد تأتي من استبدال الضوء الذي تتعرض له قبل النوم بالضوء الأحمر, بدلاً من إضافة الأخير أثناء النوم. "وقد يكون هذا هو ما يؤدي إلى نوم أفضل."
لأن الضوء الأحمر لا يؤثر على النظام اليومي, إمكانية الضوء الأحمر للحث على اليقظة, كما وجدت فيجويرو في بحثها, "من المرجح أن يؤثر على دماغك من خلال مسارات أخرى غير الساعة البيولوجية,قالت. نظام الساعة البيولوجية ويقظة الدماغ ليسا نفس الشيء.
لكي يتأثر الميلاتونين أو إيقاع الساعة البيولوجية بالضوء, يجب أن يكون هناك ضوء يمر عبر النوى فوق التصالبية - وهي بنية الدماغ حيث تقع الساعة البيولوجية - ويثير استجابة يومية, وأضاف فيجويرو.
الضوء الأحمر عمومًا لا يفعل ذلك, لذلك "ما نعتقد أنه يحدث هو (الضوء الأحمر) هو في الواقع يؤثر على أجزاء من الدماغ المرتبطة بها, على سبيل المثال, مع النظام البصري,قال فيجويرو. "أو يمكن أن يكون مرتبطًا باللوزة الدماغية أو أجزاء أخرى من الدماغ لا تمر بالضرورة عبر الساعة البيولوجية."
إجمالي, في حين أن الضوء الأحمر لا يعزز بالضرورة النوم, فهو أقل إزعاجًا من أنواع الضوء الأخرى, قال الخبراء.
خلاصة القول هي أنه عندما يتعلق الأمر بالنوم, "ما هو أفضل من الضوء الأحمر هو عدم وجود ضوء,قال داسغوبتا. ولكن إذا كنت ستحصل على الضوء, مثل ضوء الليل, لأي سبب من الأسباب أثناء النوم, يمكنك أيضًا استخدام تلك التي ستكون أكثر ملاءمة للنوم, وأضاف - حيث يمكن أن يكون الضوء الأحمر مفيدًا.