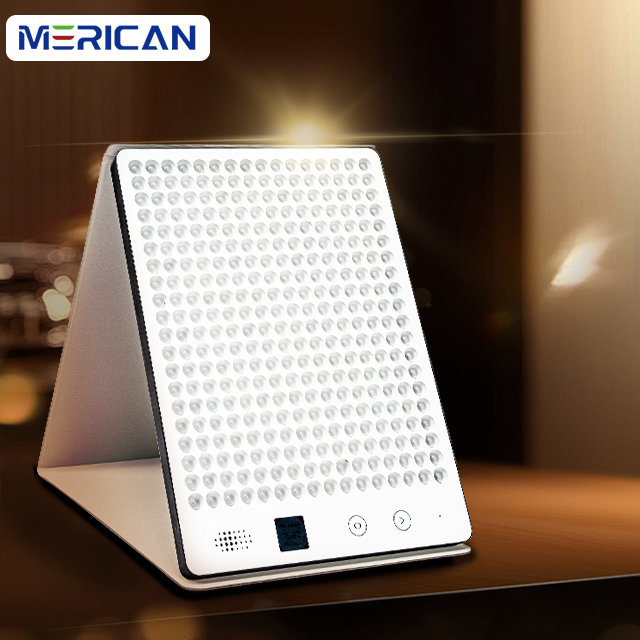
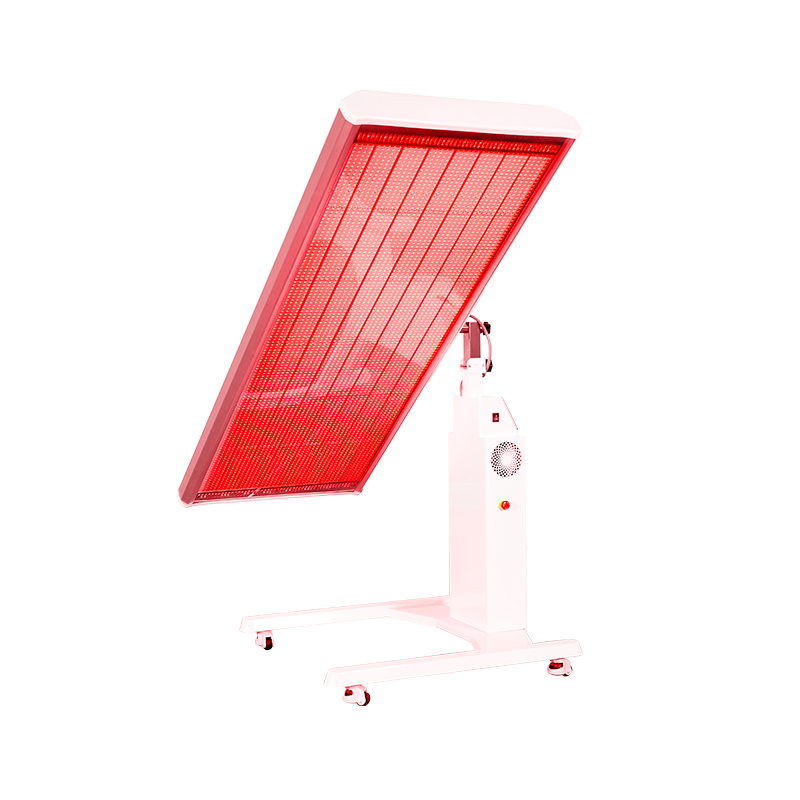
Diabete mellito, una malattia cronica in cui anomalie degli ormoni endocrini causano concentrazioni eccessive di glucosio nel sangue, scatenando danni multiorgano.
Il numero di adulti invecchiati 20-79 anni con il diabete a livello globale in 2021 è enorme 537 milioni, O 7 fuori 100 persone con diabete. Evitare il cibo, misurare la glicemia e assumere insulina ogni giorno porta innumerevoli problemi di vita e ansia psicologica alla maggior parte dei pazienti e alle loro famiglie.
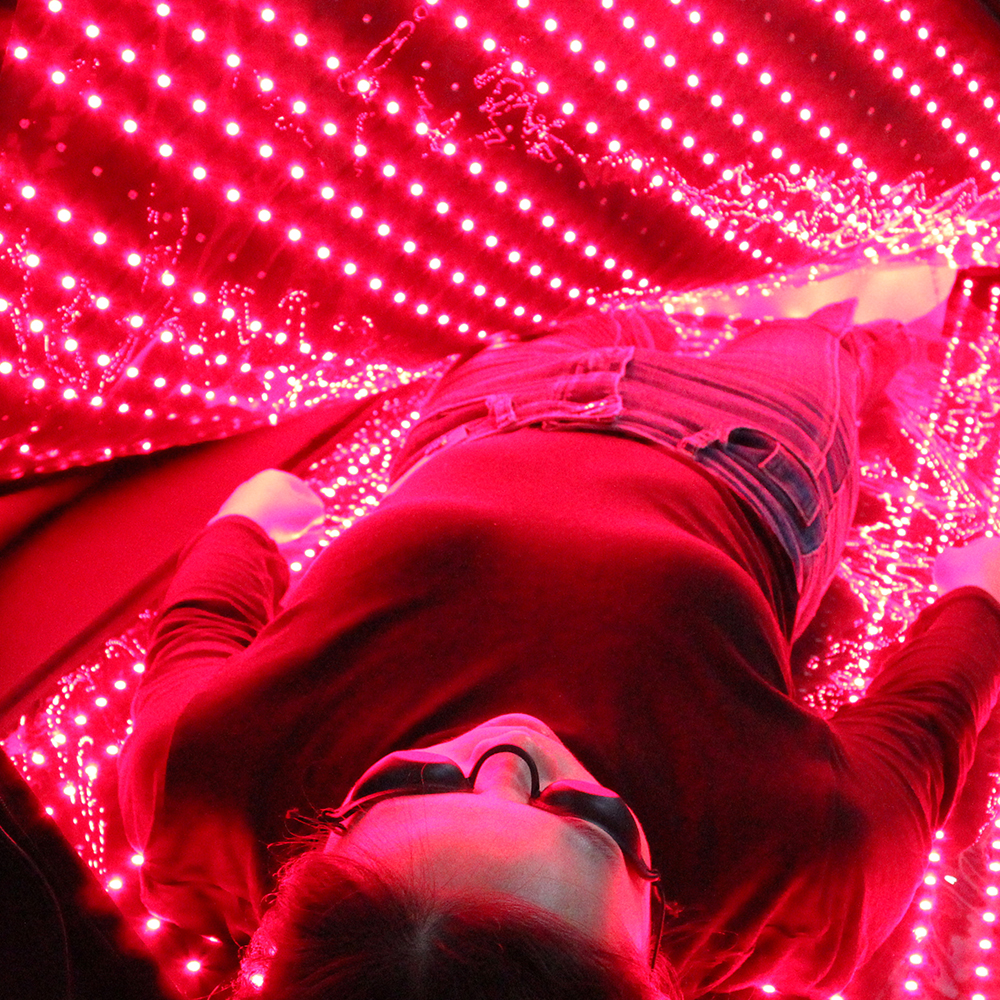
Fortunatamente, “Science and Technology Daily” ha recentemente dato una notizia pesante, alla maggior parte degli “amici dello zucchero” per portare del bene: City College di Londra, Lo dimostra la collaborazione tra gli scienziati dell'Università di Londra e dell'University College di Londra per portare avanti le ultime ricerche 670 irradiazione di luce rossa nanometrica nella schiena di una persona per 15 minuti, può ridurre i livelli di zucchero nel sangue!
L'irradiazione della luce rossa riduce la devastazione dello zucchero nel sangue
Il diabete in sé non è spaventoso, sono le complicazioni che fanno paura, e il DCCT (Prova sul controllo e sulle complicanze del diabete) e studi europei hanno da tempo confermato che il controllo dello zucchero nel sangue può effettivamente rallentare lo sviluppo di complicanze in entrambi i tipi 1 e digitare 2 diabete.
L’approccio usuale per controllare la glicemia è l’intervento sullo stile di vita con la somministrazione orale di qualche tipo di farmaco ipoglicemizzante. Tuttavia, man mano che la malattia progredisce, diventerà sempre più difficile abbassare la glicemia, e molteplici agenti ipoglicemizzanti, anche l'insulina, sarà gradualmente necessario per controllare la glicemia. Questi trattamenti farmacologici invasivi possono portare effetti collaterali inaspettati ai pazienti. E come non invasivo, tecnica non farmacologica nota per la sua sicurezza, la fisioterapia a luci rosse ha il potenziale per ridurre al minimo gli effetti collaterali e apportare maggiori benefici ai diabetici.
A quanto pare, i mitocondri sono conosciuti come le “fabbriche di energia” cellulari, che utilizzano ossigeno e glucosio per produrre adenosina trifosfato (ATP), che fornisce energia per importanti processi cellulari nel corpo. Quando 670 la luce rossa nm stimola i mitocondri, il potenziale della membrana mitocondriale e la produzione di adenosina trifosfato (ATP) può essere aumentato attraverso la fotobiomodulazione (PBM), un processo che aumenta la domanda e il consumo di glucosio, abbassando così i livelli di glucosio nel sangue.
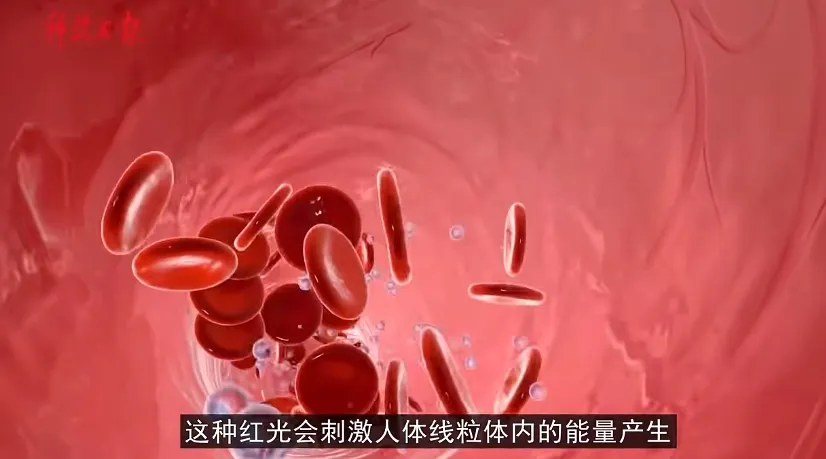
Gli esperimenti hanno dimostrato che questa stimolazione della luce rossa riduce i livelli di glucosio nel sangue 27.7% dopo l'ingestione di glucosio e la riduzione dei picchi massimi di glucosio 7.5%. Secondo il Dott. Bonner, l'autore principale dello studio, dice che possiamo usare una singola esposizione di 15 minuti alla luce rossa dopo aver mangiato per aiutare a ridurre i picchi di glucosio potenzialmente dannosi nel corpo dopo un pasto.
Questo ultimo studio, pubblicato sul giornale tedesco di biofotonica, una delle principali riviste scientifiche internazionali, lo suggerisce Sebbene questo studio sia stato condotto su individui sani, è non invasivo, La tecnica non farmacologica ha il potenziale per avere un impatto positivo sul controllo del diabete postprandiale riducendo le fluttuazioni dannose dello zucchero nel sangue nel corpo che portano all’invecchiamento.
Dott. Bonner, Docente senior di Neurobiologia presso la Scuola di Scienze della Salute e Psicologiche della City, e il professor Geoffrey, Professore di Neuroscienze presso l'Istituto di Oftalmologia, University College di Londra, ha anche detto che questo miglioramento nella produzione di adenosina trifosfato (ATP) dai nucleosidi porta a cambiamenti nella segnalazione che si propagano in tutto il corpo.
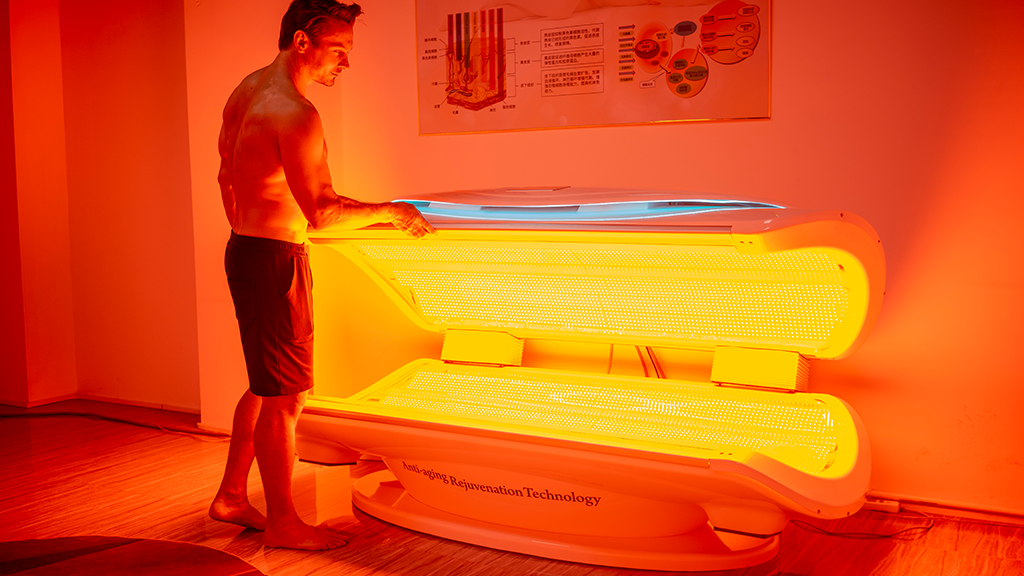
La luce rossa è ampiamente utilizzata nella terapia ricreativa
Fotobiomodulazione (PBM) della luce rossa è principalmente fotochimica, non termico. L'effetto ottenuto dall'irradiazione della luce rossa avviene principalmente attraverso il trasferimento dell'energia della luce rossa nelle cellule per stimolare una nuova vitalità cellulare.
Precedenti studi autorevoli hanno confermato che la luce a lunga lunghezza d'onda è compresa tra circa 650-900 nm (dalla gamma del visibile al vicino infrarosso) aumenta la produzione di ATP mitocondriale, che abbassa la glicemia e migliora la salute e la longevità degli animali. Negli studi precedenti, 670 È stato dimostrato che la luce nm irradiata selettivamente sulla schiena dei topi migliora l'ATP, e quindi i sintomi, sia in un modello di malattia di Parkinson che in un modello di retinopatia diabetica.

Il massimo assorbimento della luce rossa sono i mitocondri, l'irradiazione della luce rossa aumenta l'attività della catalasi nei mitocondri, che può aumentare il metabolismo cellulare, aumentare il contenuto di glicogeno (non solo immagazzina energia, ma si scompone anche in glucosio per regolare la concentrazione di glucosio nel sangue), aumentare la sintesi delle proteine e aumentare la decomposizione dell'adenosina trifosfato per promuovere la sintesi cellulare, guarigione di ferite e ulcere, crescita dei capelli e guarigione delle fratture ossee, accelerare la rigenerazione dei nervi danneggiati, aumentare la fagocitosi dei globuli bianchi, rimuovere i radicali liberi nel corpo, in modo che la viscosità del sangue diminuisca e la capacità di trasporto dell'ossigeno aumenti significativamente, regolare la funzione immunitaria, migliorare l'accumulo di grasso, ritardare l'invecchiamento cutaneo, quindi la luce rossa in clinica può curare una varietà di malattie.

Come non invasivo, tecnologia non farmaceutica, la fisioterapia a luci rosse è innocua e viene utilizzata da molti grandi ospedali terziari per dare sollievo ai pazienti’ Dolore.
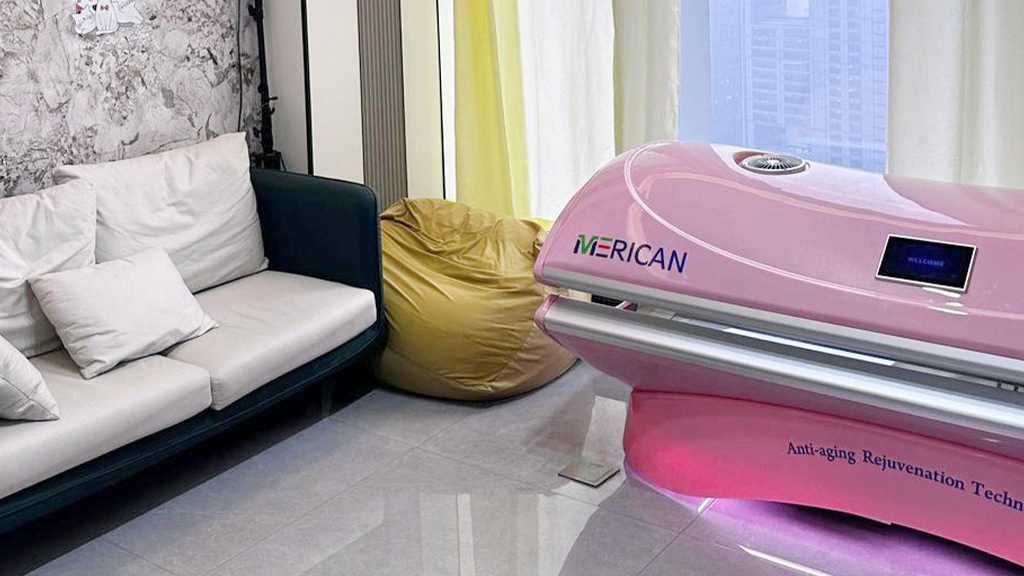
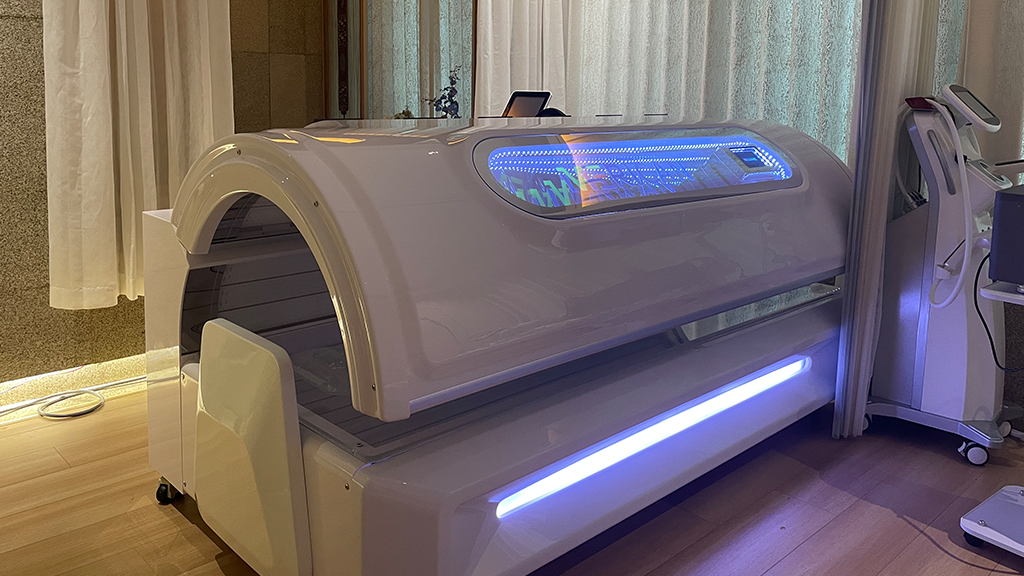
Merican Light Energy Research Center e numerose università, istituti di ricerca medica attraverso una serie di verifiche cliniche hanno anche dimostrato che attraverso una sorta di irradiazione di luce rossa chiamata cabina sanitaria fotodinamica, può penetrare 1-4 cm sotto la pelle, sul miglioramento delle malattie cardiovascolari e cerebrovascolari e di altre malattie del sistema circolatorio, riparazione del dolore tissutale e nervoso, riabilitazione postpartum, così come restauro fisico e chirurgia estetica e così via, ci sono effetti evidenti. Insieme all'utilizzo della sorgente di luce fredda LED, modo del diodo luminescente per la sorgente luminosa, low heat generation, no thermal radiation, even if beyond the treatment time, will not produce thermal damage to the human body, and does not contain any radioactive substances.



























